Insulators
Introduction
Insulators are used to isolate and fix output terminals to the element. They are generally used where the insulation voltage or operating voltage exceeds 4 KV, or when the low number of outputs makes it more economical to use them instead of a plate for fixing lugs or bars. There are many different types of insulators. A standard insulators has been included here. However, it is possible to insert tables of insulators that differ quite significantly from those.
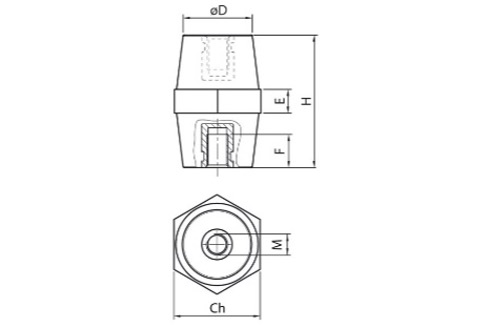
Table fields (Insulators)
- Code: code identifying the type of insulators. The standard insulators shown in the drawing above corresponds to IS.
Other types of insulators will have different codes, agreed with us. - Rating voltage V: maximum-rating voltage supported.
- Hole diameter: hole diameter D. See drawing above.
- Height: insulator height H. See drawing above.
- Type: name of the insulator. Generally, the name is given to it by the supplier.
- Length: width in the key of the insulator Ch. See drawing above.
- Lower thread depth: thread depth F. See drawing above.
- Force Nm: the field for future use. Do not fill in.
- M upper screw: M size of the lower internal thread. See drawing above.
- Upper thread depth: depth of the upper thread. The upper hole may not exist, depending on the insulator model.
- Standard: enter YES if the dimensions are standard, i.e., part of a supplier's STD series.
- Lower screw M: M size of the lover internal thread. The top hole may not exist, depending on the insulator model.
- Article: to select the material, use the article code of your management system. This value will allow the applications to retrieve the description and unit cost into the table Material Unit Cost by importing the list of materials available in your warehouse.